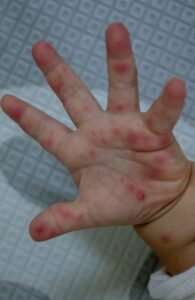
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness affecting children. In most cases, HFMD can be managed at home with symptomatic treatment, and hospitalization is usually not necessary. This article provides practical advice on how to care for a child with HFMD at home, helping to ease their discomfort and ensure proper care.
1. Symptomatic Treatment
Fever and Sedation
HFMD often comes with a fever. If the child's temperature exceeds 38.5°C (101.3°F), physical methods like tepid sponging or cooling patches can be used, or antipyretic medications (such as acetaminophen) can be given. Ensure the child stays comfortable to avoid febrile seizures. If necessary, anticonvulsant medications like chloral hydrate can be used.
Isolation and Hygiene
To prevent the spread of the virus, keep the infected child away from other healthy children. Maintain cleanliness in the child's room, wash hands regularly, and ensure the child's personal items are sanitized.
2. Diet and Oral Care
Bland Diet
Offer easily digestible and mild foods, avoiding spicy, greasy, or irritating foods. It's recommended to give the child porridge, steamed eggs, and clear soups, while ensuring adequate hydration to prevent dehydration.
Oral and Skin Care
Keep the child’s mouth and skin clean to prevent secondary infections. Use warm water to help the child rinse their mouth, and clean the skin around the blisters regularly to prevent scratching and infection.
3. Medication Treatment
Early-Stage Medications
Although there is no specific antiviral medication for HFMD, some drugs can help relieve symptoms. For example, interferon alpha can be administered via spray or nebulization to combat the virus. Ribavirin may be effective when used early, but attention must be paid to its potential side effects and reproductive toxicity.
Treatment for Severe Cases
In more severe cases, more intensive treatments may be needed, such as using mannitol to reduce intracranial pressure, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) to support the immune system. If the child experiences severe symptoms like breathing difficulty or persistent high fever, professional medical help should be sought immediately.
4. Medications to Avoid
Medications Not Recommended
Although some drugs like acyclovir, ganciclovir, and adenosine monophosphate are used for other viral diseases, there is insufficient evidence to support their efficacy against HFMD. Additionally, they may have adverse effects, so their use is not recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What are the symptoms of HFMD?
Common symptoms of HFMD include fever, small blisters in the mouth, and rashes on the hands and feet. Most symptoms are mild and usually resolve within one to two weeks.
Q2: Is HFMD contagious?
Yes, HFMD is highly contagious as it is caused by enteroviruses. The virus can spread through direct contact, respiratory droplets, or contact with the infected person’s belongings.
Q3: What should my child eat if they have HFMD?
Offer bland, easy-to-digest foods like porridge, soups, and steamed eggs. Avoid spicy and irritating foods. Make sure the child stays hydrated to prevent dehydration.
Q4: Does HFMD require hospitalization?
Most cases of HFMD can be managed at home with symptomatic treatment. However, if symptoms worsen or complications such as difficulty breathing or persistent high fever occur, medical attention should be sought.
Q5: How can I prevent HFMD?
Maintain good personal hygiene, especially handwashing. Avoid close contact with infected individuals, and do not share utensils or personal items.
Key Takeways
Most children with HFMD can recover at home with appropriate symptomatic treatment. By following proper care guidelines, maintaining good hygiene, and following the advice of a healthcare professional, parents can help their child recover faster. However, if the child’s condition worsens or complications arise, it’s crucial to seek professional medical help.
References: