HFMD is mainly caused by enteroviruses. These viruses enter the child's body through the digestive or respiratory tract. Once inside, they multiply in the tonsils, throat, and intestinal cells, spreading the infection throughout the body.
Risk Factors for Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
HFMD primarily affects infants and young children with weaker immune systems. It is especially contagious in settings where children are in close contact, like daycare centers or kindergartens. The disease spreads through contact with contaminated hands, toys, food, or close interaction with asymptomatic carriers.
Typical Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
1. Rash Phase Symptoms:
- Incubation Period: The incubation period for HFMD is usually 2 to 10 days, with an average of 3 to 5 days.
- Early Signs: In the first few days, children may feel tired, have a reduced appetite, mild fever, and general discomfort.
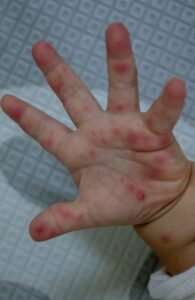
- Rash Development: After 1 to 2 days of fever, small painful blisters can appear inside the mouth. Red spots or blisters may develop on the hands, feet, and buttocks. Some children may only have a rash or herpangina (a type of throat infection with blisters), while others may not have a rash at all.
2. Nervous System Involvement Symptoms:
- Onset: In rare cases, the virus can affect the central nervous system within 1 to 5 days of illness.
- Symptoms: This can cause symptoms such as headaches, vomiting, irritability, tremors, and muscle weakness, resembling conditions like meningitis or encephalitis.
3. Pre-heart and Lung Failure Symptoms:
- Onset: Typically within the first 5 days of illness.
- Symptoms: Children may exhibit rapid heart rate and breathing, cold sweats, cool extremities, and elevated blood pressure. This stage is critical in severe cases, and early detection and treatment are crucial.
4. Heart and Lung Failure Symptoms:
- Symptoms: Children might show signs of rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, purple lips, and coughing up pink frothy sputum or bloody fluid. Severe cases can lead to a drop in blood pressure, shock, and unstable vital signs, posing a life-threatening risk.
5. Recovery Phase Symptoms:
- Improvement: During recovery, the child's temperature gradually returns to normal, and their dependency on medications decreases.
- Restoration: Nervous system and heart-lung functions slowly return to normal. In rare cases, there may be lingering neurological effects. About 2 to 4 weeks after the illness, children may also experience nail shedding (onychomadesis).