What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness primarily affecting infants and children under 5 years old. It is caused by enteroviruses, and it typically occurs during hot and humid seasons. Its peak period usually occurs in the summer and autumn, particularly between June and September, when the warm and humid climate provides favorable conditions for the spread of the virus.
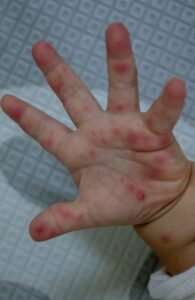
The disease is characterized by fever, rashes, and small blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth. While most cases are mild, complications such as meningitis, encephalitis, respiratory infections, and myocarditis can occur. In severe cases, HFMD can progress rapidly and be fatal.
How is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Spread?
Transmission Sources:
HFMD spreads through various channels, including:
- Close Contact: The virus can spread through contact with the infected person’s feces, saliva, nasal discharge, and blister fluid.
- Respiratory Droplets: The virus is also transmitted when an infected person coughs or sneezes, releasing droplets that others can inhale.
- Contaminated Food and Water: Eating food or drinking water contaminated with the virus can also cause infection.
Transmission Routes:
- Direct Contact:
- Contact with the infected person’s saliva, nasal secretions, or blister fluid.
- Touching contaminated items such as toys, towels, or clothing.
- Direct contact with skin rashes.
- Respiratory Droplet Transmission:
- The virus can spread when an infected person coughs or sneezes, releasing droplets into the air.
- Food and Water Transmission:
- Eating food or using utensils contaminated by the virus.
- Drinking contaminated water.
Who is at Risk for Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
High-Risk Groups:
- Infants and children under 5 years old are most susceptible to HFMD, though adults can also contract the virus.
High-Risk Areas:
HFMD occurs globally, with no clear regional patterns. It is more common in tropical and subtropical regions year-round, and there is a peak in temperate areas during the summer and autumn months.
Prevention Tips:
HFMD is highly contagious, but it can be prevented by taking the following measures:
- Good Hygiene:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom and before eating.
- Avoiding direct contact with infected individuals, especially during outbreaks.
- Cleaning and Sanitizing:
- Regularly disinfecting toys, clothes, and frequently touched surfaces to minimize the virus’s spread.
- Properly washing utensils and dishes used by the infected person.
- Avoiding Crowded Places:
- If a child is infected, keep them home from school or daycare to prevent spreading the virus to others.
Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
The symptoms of HFMD include:
- Fever: Often the first symptom, followed by the appearance of a rash.
- Rashes and Blisters: Red, non-itchy rashes appear on the hands, feet, and sometimes the buttocks. Small, painful blisters may develop, especially in the mouth.
- Mouth Sores: Painful sores in the mouth, which may make eating and drinking difficult.
- Other Symptoms: Loss of appetite, irritability, and a general feeling of discomfort.
How to Treat Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HFMD. The condition typically resolves on its own in 7-10 days. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms:
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and fever.
- Hydration: Encourage the child to drink plenty of fluids, especially if mouth sores make swallowing painful.
- Topical Relief: Use soothing lotions or ointments to alleviate the discomfort from rashes or blisters.
When to Seek Medical Help?
In most cases, HFMD is mild and self-limiting. However, you should seek medical attention if your child:
- Experiences high fever that doesn’t subside with medication.
- Shows signs of dehydration (e.g., dry mouth, reduced urine output).
- Has difficulty breathing or exhibits neurological symptoms (e.g., seizures, persistent vomiting).
The Takeaway : How to Protect Your Child from Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
HFMD is highly contagious but preventable with proper hygiene and care. Infants and young children are most at risk, so it is important for parents and caregivers to be vigilant about cleaning, avoiding exposure to infected individuals, and seeking prompt medical care if symptoms arise.
By maintaining good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and ensuring a clean environment, you can significantly reduce the risk of HFMD spreading in your home.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease contagious?
Yes, HFMD is highly contagious. It can spread through direct contact with an infected person’s bodily fluids, such as saliva, mucus, and blister fluid, as well as through contaminated food or water.
2. How long does Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease last?
HFMD typically lasts 7-10 days. Most children recover without needing any special treatment, although some symptoms, like mouth sores and fever, may last a bit longer.
3. Can adults get Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Yes, although it primarily affects children under the age of 5, adults can also contract HFMD. However, adults usually experience milder symptoms.
4. What are the main symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Common symptoms include fever, red rash with blisters on the hands, feet, and buttocks, mouth sores, loss of appetite, and irritability.
5. How can I prevent my child from getting HFMD?
Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water, disinfecting commonly touched surfaces, and avoiding contact with infected individuals, can help prevent the spread of HFMD.
6. When should I take my child to the doctor for HFMD?
You should seek medical attention if your child experiences a high fever that doesn’t subside, signs of dehydration (dry mouth, less urination), or severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or neurological issues like seizures.
7. Is there a vaccine for Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent HFMD. Preventive measures mainly focus on good hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals.
8. How is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease treated?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HFMD. Treatment mainly focuses on relieving symptoms, such as using fever-reducing medications, ensuring hydration, and soothing mouth sores with topical gels.
References:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- Mayo Clinic – Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease